The learning process of grades 1-4 in the PYP
The role in the development of students in the Primary Years Programme (PYP)
The Critical Thinking System (CTS) plays a vital role in the development of students in the IB Primary Years Programme (PYP). It is integrated into the learning process and provides students with the following key benefits:
1. Development of thinking skills: CTS teaches students to analyze information, identify connections, and make well-founded conclusions. They don’t just memorize facts but learn to consider problems from different perspectives, leading to a deeper understanding.
2. Building research skills: In PYP, students ask questions and seek answers. CTS helps them develop their research skills, encouraging independent exploration of topics, which fosters curiosity and confidence in their abilities.
3. Increased engagement: Critical thinking makes the learning process more interactive and engaging. Students participate in discussions, analyze different viewpoints, and develop their own opinions and arguments, maintaining high levels of motivation and interest.
4. Problem-solving ability: Using CTS, students learn to break complex problems into manageable steps. This enhances their ability to find solutions to challenging issues through critical analysis.
5. Openness and creativity: CTS fosters flexibility in thinking. Students learn to be open to new ideas, think creatively, and go beyond conventional thinking, helping them adapt to new situations and challenges.
6. Development of metacognitive skills: PYP students also learn to evaluate their own thinking processes. They ask themselves questions like, “Why do I think this way?”, “What evidence do I have?”, and “What do I need to learn?”. This helps develop self-reflection and self-regulation skills that are crucial for continuous improvement.
7. Empathy and collaboration: CTS helps students understand and respect different viewpoints, fostering empathy and effective teamwork skills. During discussions and idea exchanges, students learn to work in teams and make decisions collaboratively.
Thus, CTS in the PYP context supports not only academic growth but also the development of essential life skills, such as creativity, adaptability, self-improvement, and teamwork.
PYP Direction Work in the 2024-25 Academic Year
At present, the school has successfully completed the Consultation Visit for the PYP program and is now preparing for authorization. The main areas of work being carried out in accordance with the program’s requirements are:
- Primary school teachers undergoing professional development courses;
- Development and implementation of an Action Plan for integrating the main standards and elements of the PYP program;
- Creation and work on the Program of Inquiry for the PYP, including working with Unit Planners;
- Establishment and implementation of an assessment system;
- Initiation of work on the key PYP project — the PYP Exhibition;
- Equipping the library with resources (multimedia and book collections) and having the librarian undergo professional development courses, along with developing and implementing an Action Plan for the library.
Study Load
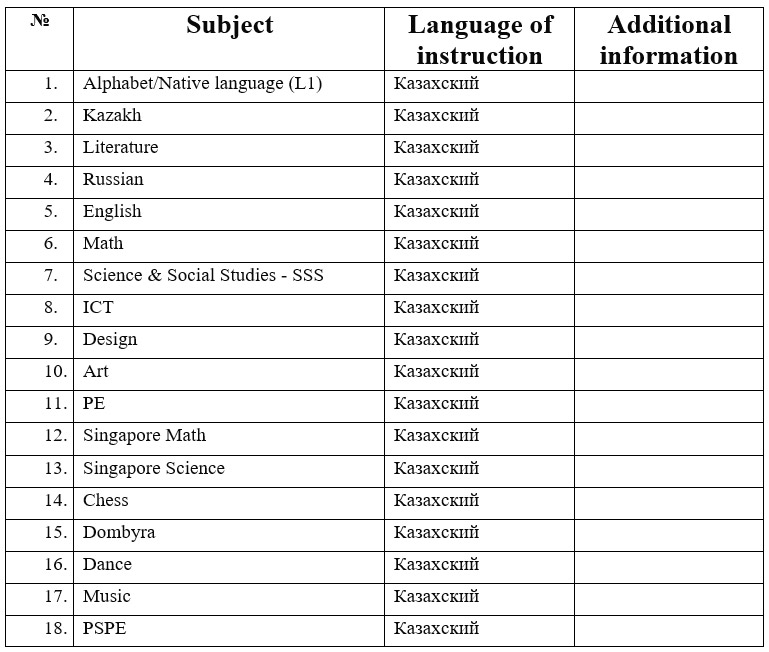
Assessment system (in accordance with Order No. 125)
Chapter 2. Procedure for conducting current performance monitoring of students
6. Student achievement is assessed through formative and summative assessments. Formative assessment results are presented as scores in the students’ completed work and/or in electronic journals, and the teacher may provide comments.
7. Current performance monitoring of students is conducted by teachers in the form of summative assessments after the completion of a quarter or a unit (common theme) to determine and monitor the level of mastery of the learning material.
8. Students in grades 2-11 receive scores based on formative assessment, summative assessment for a unit/common theme (hereinafter — SAU), and summative assessment for the quarter (hereinafter — SAQ), which are taken into account when evaluating the students’ academic achievements for the quarter.
Scale for converting scores into grades
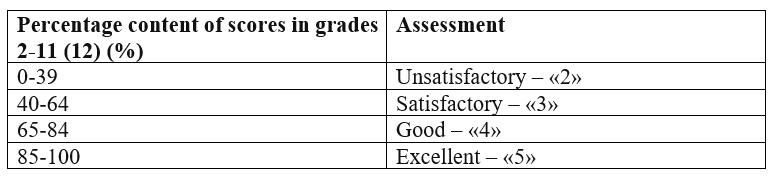
Assessment criteria description
Fully Mastered (FM) - 5
Ученик полностью осваивает учебные цели и навыки и понимает все значения. Он может применять свои знания и навыки. С критическим мышлением приходит к конкретному решению. Может понятно донести своё решение. В учебном процессе ученик проявляет самостоятельность и может работать индивидуально.
Foundations Mastered (FM) - 4
Ученик осваивает большинство учебных целей и навыков и понимает большинство значений. Иногда возникают трудности при применении своих знаний и навыков. С критическим мышлением часто приходит к конкретному решению. Может донести своё решение понятно, но иногда испытывает трудности. В учебном процессе ученик проявляет самостоятельность, иногда обращается за помощью к учителю.
Partially Mastered (PM) - 3
Ученик частично осваивает учебные цели и навыки и испытывает трудности с пониманием значений. Возникают трудности при применении своих знаний и навыков. Пытается прийти к конкретному решению. Испытывает трудности с донесением своего решения, но находится в процессе обучения. В учебном процессе ученик часто обращается за помощью к учителю.
Not Mastered (NM) - 2
Ученик не освоил большинство учебных целей и навыков и испытывает трудности с пониманием значений. Испытывает трудности при применении своих знаний и навыков. Не может прийти к правильному решению. В учебном процессе ученик обращается только за помощью к учителю.
Not Assessed - NA
Not assessed because the section of the program indicated in the report has not been covered with the students / not assessed due to the student’s absence from classes.
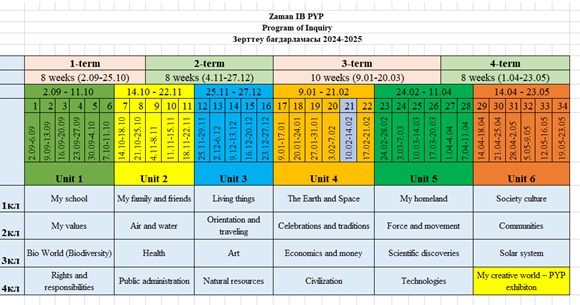
Program of Inquiry 2024-2025